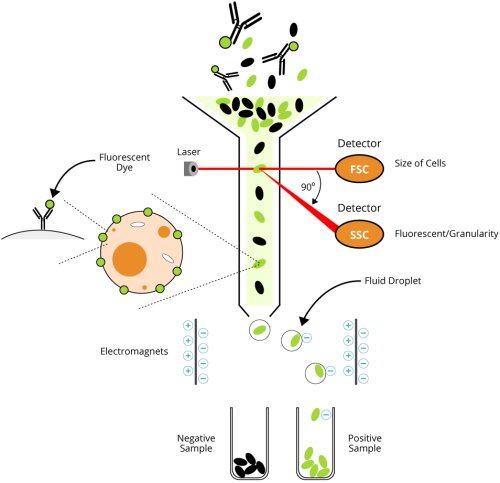
In the context of Flow cytometry, Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) is a method that is utilized in differentiating and sorting a sample of a mixture of biological cells. The cells are separated from two or more containers. The sorting method is based on the physical features of the cell which includes light scattering and fluorescence characteristics of the cell. This is an important scientific technique, which can be utilized to obtain reliable quantitative and qualitative results of fluorescence signals that are emitted from each cell. During FACS, initially, the pre-obtained mixture of cells; a suspension is directed to the center of a narrow stream of liquid which is flowing swiftly. The flow of liquid is designed in order to separate the cells in the suspension based on the diameter of each cell. A mechanism of vibration is applied to the stream of suspension which results in the formation of individual droplets.