Read the abstracts of the recent PhD defences at the Department of Regional and Urban Economics.
PhD Under preparation
- Dan Behr (Behr & Associates): Investigation of the financial viability of establishing a European version of the US-style "short-line" freight railway, operating over selected corridors, through regions within the EU
- Peter Bulckaert: Key factors in determining the success or failure of start-up airlines
- Chan Kwok: Air cargo capacity and revenue management in the era of overcapacity
- Elnert Coenegrachts: Shared mobility providers – Enabling sustainable urban mobility?
- Da Fonseca Nunes Marques: Transition from conventional vehicle taxation models in light of emerging energy and powertrain technologies: a system dynamics approach
- Koen De Winne: Haveninvesteringen als beleidsinstrument: strategische beleidsbeslissingen in complexe havenomgevingen
- Masoud Gargari: Shipberthing allocation and speed optimization
- Eva Jung: The Integration of Ports in Sustainable Multimodal Freight Transport Modelling for the Plastic Recycling Industry
- Bruce Lambert: Does the presence of a ‘super-individual’ change the evaluation of potential benefits for public sector participation in multimodal freight (maritime) corridors?
- Osvaldo Navarro: Evaluation of urban logistics policy measures
- Loghman Nanwayboukani: The economics of vessel platooning
- Periklis Saragiotis: Maritime trade regulatory impact analysis
- Daniel Schubert: Real options analysis to validate and assess risk of road and/or rail fixed links, bridges and tunnels
- Peter Shobayo: A holistic approach to barge congestion in large seaports
- Aanan Sutaria: last-mile delivery with micro hubs
- Bassam Tariq Malik: Welfare economic impact of airline joint ventures
- Ruben Van Deuren: Analysis and optimidationh of the non-optimal use of inland shipping
- Thomas Verlinden: Optimization and cost analysis of multi-drop and social logistics in the Ho.Re.Ca. and health care sector in an urban context
- Michiel Voes: Guidelines for passenger rail operators to become competitive in a liberalized passenger rail market
- Spyros Vougios (BCA Business School, Athens): The ship demolition market and its impact to the economics of the shipping industry
PhD Sisangile Nduna - 18 maart 2022
On 18 March 2021 at 4pm, Sisangile Nduna succesfully defended her PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Efficiency and productivity in container terminal operation: A case study for the Hamburg - Le Havre range', Supervisors: Prof. dr. Thierry Vanelslander.


Sisangile Nduna Kindly invites you to the public defence of her doctoral thesis.
Efficiency and productivity in container terminal operation: A case study for the Hamburg – Le Havre range
Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Thierry Vanelslander – University of Antwerp
Friday 18 March 2022 at 4 p.m.
Promotion Hall – Cloister of the Grauwzusters
University of Antwerp, City Campus
Lange Sint-Annastraat 7, 2000 Antwerp
Due to Covid-19 regulations, there will be limited seats. A face mask and a Covid Safe Ticket are also mandatory for participants. Please contact Ms. Sisangile Nduna (Sisangile.Nduna@uantwerpen.be) to inform her whether you wish to attend the PhD defence physically or online through MS Teams before Wednesday 16 March 2022.
Efficiency and productivity in container terminal operation: A case study for the Hamburg – Le Havre range
The container sector's significance dates back to the 1950s. Times of economic turmoil, such as the 2008 financial crisis, the COVID-19 Pandemic, the 2021 Suez Canal blockade, are recent phenomena where the importance of the maritime and port sector became visible to the general public. As an exchange interface, terminals handle hundreds of millions of containers every year to facilitate trade and globalisation. Efficiency and productivity at container terminals are highly driven by frequent port calls, resilient infrastructure and adequate accessibility through the hinterlands. Investments in the infrastructure and the superstructure by terminals can save customers a large amount of costs.
This thesis addresses the role of infrastructure and superstructure in evaluating efficiency in container terminals. The role of port competition is addressed to indicate implications of closeby terminals and ports to performance. The implications due to performance can also be observed through costs, an element also investigated in this thesis. The methodological approach used for perfomance includes non-parametric and parametric methods to conclude. The analysis for productivity and efficiency is through the use of the Malmquist productivity Index (MPI) and the data envelopment analysis (DEA) (Charnes, Cooper and Rhodes (CCR) and Banker, Charnes and Cooper (BCC)). To evaluate the association of the external factors with the relative technical efficiency of the terminals, the Tobit regression and the Kruskal – Wallis models are used. The methods are applied in the Hamburg Le-Havre (HLH) context considering two periods, 2013 and 2018. For the costs analysis, only the terminals at the port of Antwerp are evaluated.
The emphasis in efficient handling of resources is identified as key in the functioning of the business. The external factors are recognised as additional major contributing factors to the container handling business. Through efficient handling of containers, terminal operators can save costs, not only for themselves, but also for the rest of the stakeholders. The outcomes indicate that relative efficiency is vital to evaluate especially in a business environment where competition is high. The HLH is found to maintain a positive trend of productivity and efficiency over the time measured. Scale inefficiencies contribute negatively to the overall efficiency in the region. The high efficiency and productivity in the region indicate proper management of resources by the terminal managers, which suggests that the capacity expansion investments are paying off. Although it is proven that environmental factors are not highly significant in terminals in close proximity, it is also emphasised that the external factors are generally substantial in shaping cargo flows, which is vital in determining efficiency.
In addressing the measurement and importance of terminal efficiency, this research provides insight to container terminal managers on effective ways to manage resources at their terminals. The research contributes by providing a holistic view of terminal handling to policymakers for large investment decision-making purposes. Research focusing on the terminal level, especially in a region with business operation characteristics such as the HLH, is limited thus this work helps to reduce that gap.
PhD Seyed Abolfazl (Majid) Mohseni - 25 januari 2022
On 25 January at 4pm, Majid (Seyed Abolfazl) Mohseni succesfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Sustainability of maritime supply chain; economic analysis to comply with environmental regulations and social issues', Supervisors: Prof. dr. Hilde Meersman & Prof. dr. Edwin van Hassel


Majid (Seyed Abolfazl) Mohseni
Kindly invites you to the public defence of his doctoral thesis.
Sustainability of maritime supply chain; economic analysis to comply with environmental regulations and social issues
Supervisors:
Prof. Dr. Thierry Vanelslander – University of Antwerp
Prof. Dr. Edwin van Hassel – University of Antwerp
Tuesday 25 January 2022 at 4 p.m.
Room Willem Elsschot – Hof van Liere
University of Antwerp, City Campus
Prinsstraat 13, 2000 Antwerp
Due to Covid-19 regulations external guests are not allowed. Please contact Mr. Majid (Seyed Abolfazl) Mohseni ( seyedabolfazl.mohseni@uantwerpen.be ) to inform him whether you wish to attend the PhD defence online through MS Teams before Friday 21 January 2022.
Sustainability of maritime supply chain; economic analysis to comply with environmental regulations and social issues
Maritime transport is considered the most significant transport mode in world trade and maritime trade have risen in recent years, which leads to economic growth. However, at the same time, it causes severe environmental effects that jeopardize the ecosystem and human health. The adverse impacts of the maritime supply chain (MarSC) are not limited to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and air pollution, but they include other significant issues such as the spread of invasive species via ballast water, oil spill, chemical and waste management, cargo handling, safety and security at the ports, and noise pollution.
The sustainability of this sector is a challenging issue for the stakeholders involved in this industry. Several aspects are indispensable to enhancing the sustainability of MarSC, grouped as economic, social, and environmental elements. In this thesis, some of the main significant issues in containerized maritime shipping are addressed economically, in which the main objective is to improve the sustainability of MarSC under environmental and social regulations. This Ph.D. covers different segments and stages of the MarSC, including hinterland transport, seawaters, maritime shipping, and port and terminal operations to improve the sustainability of the MarSC at regional, national, and global levels.
The main objective of this Ph.D. is to provide the economic assessment of the most selected and promising technologies and methodologies to overcome the negative impacts of the marine shipping and port industry and bridge some of the available shortcomings. Besides, it will enhance the sustainability of maritime shipping in terms of economic, environmental, and social perspectives concerning the current international conventions and legislations. The overarching research question is: What is the economic impact of sustainability issues on maritime shipping in various trade routes from different stakeholders’ standpoints?
This Ph.D. thesis is based on an application approach, and each one is researched in an independent chapter in which several methodologies are applied to fulfill the objectives and to respond to the key research question. Four main application studies are as follows: economic impact of the instalment of Same Risk Area (SRA) under the Ballast Water Management Convention (BWMC), economic evaluation of alternative technologies to mitigate sulfur emissions, enhancing the supervision of containerized cargo from an economic perspective and supply chain analysis in terms of dry and reefer cargo.
This Ph.D. supports the governments and policy-decision makers by providing the costs and benefits of selected cases of addressing the sustainability of MarSC. Moreover, the outcomes are beneficial for a large groups of maritime stakeholders including port authorities, terminal operators, customs brokers, shipping companies, shippers and academia.
PhD Eleni Moschouli - 24 november 2021
On 24 November 2021 at 4.30 pm, Eleni Moschouli succesfully defended her PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Supporting the process of transport infrastructure decision-making: an instrument to identify the combinations of conditions under which project objectives can be achived', Supervisors: Prof. dr. Thierry Vanelslander.

Eleni Moschouli
Kindly invites you to the public defence of her doctoral thesis.
Supporting the process of transport infrastructure decision-making: an instrument to identify the combinations of conditions under which project objectives can be achieved
Supervisor:
Prof. Dr. Thierry Vanelslander - University of Antwerp
Wednesday 24 November 2021 at 4.30 p.m.
Willem Elsschot Room – Hof van Liere
University of Antwerp, City Campus
Prinsstraat 13b (entrance of the University Club), 2000 Antwerp
Because of Covid-19 regulations participants need a Covid Safe Ticket
The PhD defence can also be attended online through MS Teams.
To confirm your attendance or to receive the link to attend the online PhD defence, please send an e-mail to Mrs. Eleni Moschouli ( eleni.moschouli@student.uantwerpen.be ) before Monday 22 November 2021.
Supporting the process of transport infrastructure decision-making: an instrument to identify the combinations of conditions under which project objectives can be achieved
Decision making is part of our everyday life, from simple things such as deciding what clothes to wear till more complex issues as deciding about very expensive transport infrastructure (TI) project investments. For simple decisions, we can use our intuition but for the complex decisions humans need decision support tools that will help them make a decision as rational as possible.
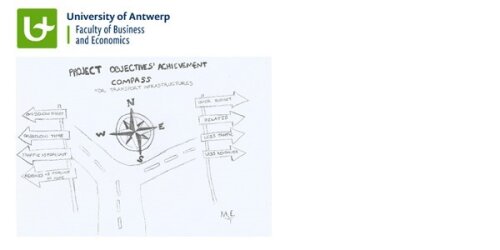
The present doctoral thesis comes to support the TI projects’ decision making process throughout the different phases of the TI projects’ lifecycle, from the early stages of planning and evaluation till the construction and operation phase, by identifying the combinations of factors that affected the performance of past TI projects. The performance of projects is defined based on four key project objectives in the present thesis, the cost, time, traffic and revenues. Thus, a TI project is considered successful, if it is delivered on the cost and time that have been initially estimated (or with less cost and in less time) and with the traffic and revenues initially forecast (or with higher traffic and revenues). A new decision support tool was developed, called ’Project objectives’ achievement compass’’ (POAC). POAC is simple to be used and understood and does not only inform its users about the likelihood that a TI project will be delivered over budget, delayed and with traffic and revenues less than they have been initially forecast but it also shows the reasons behind this failure, allowing them to try to improve the factors that have been found to be the reason of failure.
The readers of the thesis, aside to getting themselves familiar with the new decision support tool, will be shown the exact steps they should follow so as to apply it. They will be also introduced to an overall background knowledge relevant to the thesis’ topic. They will also acquire knowledge for the overall sample of cases used in the analysis and for the reasons that caused cost and time overruns, traffic and revenue underruns in each of them. In addition, the readers will be able to gain knowledge about a new indicator that has been developed in this thesis, so as to be used as one of the independent variables in the analysis and also about the fuzzy set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA) of different sub-samples of the overall sample of the 51 TI European projects. Thus, not only the readers will see how fsQCA method works and how its results are interpreted but they will also take overall conclusions out of the fsQCA results, showing the combinations of conditions (i.e. factors) under which project objectives can be achieved. The output of the present thesis can be useful for analysts, decision makers, financiers and in general for all the stakeholders that are involved in TI planning, delivery and operation and academic scholars working with similar scientific topics.
PhD Sven Buyle - 29 September 2020
On 29 September 2020 at 5pm, Sven Buyle succesfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Evolution of AIr Navigation Service Provider Business Models within the Single European Sky', Supervisors: Prof. dr. Hilde Meersman, Prof. dr. Wouter Dewulf & dr. Evy Onghena.


PhD Thomas Van Asch - 28 September 2020
On 28 September 2020 at 5pm, Thomas Van Asch succesfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Air Cargo Competitiveness and European Airports: Markets and Strategy', Supervisors: Prof. dr. Eddy Van de Voorde, Prof. dr. Wouter Dewulf & dr. Franziska Kupfer


PhD Matteo Balliauw - 24 February 2020
On 24 February 2020 at 5pm, Matteo balliauw succesfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Innovation in Inland Navigation, Failure and Succes: The European Case', Supervisors: Prof. dr. hilde Meersman & Prof. dr. Eddy Van de Voorde


Port capacity investments under uncertainty: The use of real options models
Port operations are important for worldwide and regional trade and for the development of regions. Investments in port capacity are required to perform these activities. Port infrastructure and some superstructure investments involve large sums of money, are irreversible and involve a lot of uncertainty. In the literature, real options (RO) have been identified as a methodology to improve investment decisions with a flexible size and timing under uncertainty. Elements of existing RO models from other sectors, suited for port capacity investment analyses, are combined in a framework, together with specific port-economic characteristics. Based on this, new RO port models are constructed to meet this thesis' objective, which is to study how optimal port capacity investment decisions are influenced by different port- and project-related economic characteristics under uncertainty.
In the developed models, throughput level, timing and size of the investment are flexible. As an addition to the literature, the users' congestion costs are added to the RO models for port capacity investments. Next to a base case benchmark model, a second model adds the possibility of a partially or fully publicly owned port authority (PA), as well as the division of cash flows and activities in a landlord port model between the two investing actors: the PA and the port operator. A third model adds inter-port competition to the base case model: two new ports, competing in quantities, are constructed according to a Stackelberg leader-follower model. A final model considers port expansion of one service port, as well as the construction lead time.
If port customers are on average more waiting-time averse, new port investment projects need to be developed later, and their size needs to be larger as well. In the case of port expansion, such an investment should be made earlier, whereas the impact on size is limited. Uncertainty leads to later and larger investments. Increased public ownership leads to earlier and larger investments in new ports, whereas expansions projects are even more anticipated if the public share is larger. In landlord ports, the two investing actors can agree to follow the investment strategy that would be optimal under a service port configuration. Otherwise, the PA can use the concession fee to force the terminal operator to invest in the PA's optimum. Inter-port competition reduces the option value of waiting. This leads to earlier and smaller leader investment, compared with its unrestricted strategy. The follower however will invest later and more.
PhD Edwin Verberght - 10 February 2020
On 10 February 2020 at 5pm, Edwin verberght successfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Innovation in Inland Navigation, Failure and Success: The European Case', Supervisors: Prof. dr. Thierry vanelslander & Prof. dr. Ir. Edwin Van Hassel


Innovation in Inland Navigation, Failure and Success: The European Case
European inland navigation is generally regarded to be part of the solution to road congestion. It is also the transport mode with the lowest external costs. Therefore, a strong and competitive inland navigation can be a key element in achieving climate change objectives for the transport sector. In order to remain competitive and attractive, inland navigation needs to innovate in the midst of a rapidly changing globalized logistics chain. Innovation in inland navigation is both necessary to maintain the modal share or to grow in performance, and to keep the title of the most sustainable transport mode. Alternative fuels, innovative engines and propulsion, ship design, automation and digital business applications are just a few examples of possible innovations that could provide an answer that is attractive both for the investor (industrial-economic perspective) and for society (welfare-economic perspective). Private actors play a role in this; innovation is often a story of collaboration between public and private actors within a multi-layered network to create the best conditions for successful innovation.
This doctoral dissertation focuses on innovation in European inland navigation and takes the reader on a journey into a relatively unchartered world without avoiding relatively complex networks such as the (pan-)European institutional setting. The central research question is as follows: What are the factors that determine success or failure of innovation in inland navigation and what is the role of policy?
Four cases have been analysed in order to answer the research question. The cases concern the automated inland vessel, LNG as an alternative fuel for inland navigation, e-barge chartering instead of conventional chartering and the small barge convoy to reactivate small waterways.
After a detailed and updated institutional analysis of the European multi-level governance model for inland navigation policy, a combination of analytical methods is applied where meaningful and possible within a multiple case study framework. The system innovation approach allows for mostly qualitative analysis and shows if there are any patterns during the development phases of innovation and which conditions lead the innovation to success or failure. The (social) cost-benefit analysis framework was the main source of inspiration to develop a quantitative economic analysis that includes external costs and that fits the private cost structure of an inland vessel. Innovation can bring benefits for both private and public actors or for only one of them and has implications for both actors. Finally, the role of the various policy levels, tools and their impact are analysed. This study helps investors to decide if innovation is attractive and allows policy makers to judge whether and how innovation can be supported or not and by which policy level(s).
PhD Joost Hintjens - 22 November 2019
On 22 November, 2019 at 4pm, Joost Hintjens succesfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Cooperation between seaports concerning hinterland transport' supervisors are Prof. dr. Eddy Van de Voorde and Prof. dr. Thierry Vanelslander.


Cooperation between seaports concerning hinterland transport
Seaports are, on the one hand, crucial links in the global supply network. As such, they are important sources of added value, employment and welfare. But on the other hand, they need big investments, often made with public money, and they are places where external costs are generated that are not appreciated by the communities of which they are part. Society demands from ports that in return for this ‘licence-to-operate’ the ports operate as efficiently as possible. More and more voices demand that through cooperation, this efficiency is improved, and the external costs diminished. Others believe that independence and competition is the best guarantee to make ports as efficient as possible. This thesis studies the possibilities cooperation between competing seaports can offer with a focus on port authorities and how they can cooperate in extending the hinterland.
The viewpoint is that of society, to allow the benefits of all stakeholders to be considered. A conceptual model, based on societal cost benefit analysis, is developed where the welfare effects of different cooperation strategies are analysed. More in detail, the conceptual model focusses on the social costs and benefits of combining hinterland road cargo flows of cooperating ports into a bundled transport mode, thus lowering direct and external costs and increasing the market share of the cooperating ports. This is further developed into a empiricalized cost model that combines the EU hinterland at NUTS2 level with the road cargo flows of the 104 core TEN-T ports, concluding with a tool that enables the calculation of the direct cost benefits, the effect on the value of time and the potential external cost savings of any cooperation between the 104 core ports.
The model is applied to three cooperation case scenarios. The first one consists of a bundling of the road cargo flows of the ports of the recently created North Sea Port towards the NUTS2 region of Düsseldorf. The second case concerns the bundling of the flows of the ports of Rotterdam and Antwerp towards the region surrounding Cracow. The last case calculates the effect of the modal shift facilitated by the cooperation of the four Polish ports towards their main hinterland region. From this possible cooperation strategies are suggested for the different port actors.
PhD Valentin Carlan - 20 November 2019
On 20 November, 2019 at 4pm, Valentin Carlan succesfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Maritieme supply chain innovation: costs, benefits ans cost-effectiveness of ICT introduction' supervisors are Prof. dr. Christa Sys and Prof. dr. Thierry Vanelslander.


Maritime supply chain innovation: costs, benefits and cost-effectiveness of ICT introduction
ICT innovation has become a key prerequisite for maritime supply chain (MarSC) stakeholders to remain competitive. In this context, new technological advancements from early EDI-based (electronic data interchange) solutions to contemporary blockchain-based tools are continuously changing the market. The MarSC actors need to decide which ICT solution to implement. In this process, own financial benefits are key. Equally so, the broader effects on other stakeholders participating in the chain are relevant. However, there is no comprehensive framework available to identify the costs and benefits of ICT innovation in the MarSC reported in the literature, nor applications that calculate their cost-effectiveness.
This research identifies the cost-effectiveness of integration practices introduced by ICT innovation in the MarSC. To do so, it develops, validates and applies a comprehensive costs and benefits framework taking into consideration key characteristics of ICT innovation. A collection of 44 cases provides further empirical evidence with regard to the cost and benefit elements they generate. Subsequently, four detailed cost-effectiveness analyses are carried out focusing on integration. The first analysis shows how an internal data integration practice is cost-effective for a road transport company and reduces external environmental effects at the same time. The second one studies horizontal data-integration practices in the MarSC. Focusing on data integration amongst hinterland transport operators, the analysis proves that taking a multi-disciplinary approach in building ICT innovation provides a more cost-effective outcome. The third case study focuses on vertical data integration in the MarSC. It discusses the cost-effectiveness of three strategies to implement a blockchain-based application in the MarSC that facilitates the official documents transfer. This last analysis provides evidence with regard to the increase in a community’s competitive advantage, when a mixed data integration tool is used. This tool is developed in the framework of a port community system. Overall, this dissertation provides new relevant insights with regard to costs and benefits generated by ICT innovation in the MarSC, and is valuable for both academia and industry.
PhD Katrien De Langhe - 24 September 2019
On 24 September 2019 at 5pm, Katrien De Langhe succesfully defended her PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'What role for rail urban freight distribution?' supervisors are Prof. dr. Eddy Van de Voorde and Prof. dr. Christa Sys.

PhD - Ivan Cardenas - 23 August 2019
On 23 August at 2pm, Ivan Cardenas succesfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Unlocking the benefits of pick-up points for sustainable E-commerce distribution in urban areas'.






PhD - Kostas Papoutsis - 12 July 2019
On 12 July, Kostas Papoutsis succesfully defended his PhD at the University of Antwerp, on the topic of 'Retail logistics costs and policy impact - What is the total cost to secure innovation for a greener retail supply chain?'
